Rice Nutrition: Boosting Healthy Harvests in India
When working with Rice Nutrition, the way rice plants take up, store, and use essential nutrients from soil, water, and fertilizer. Also known as paddy nutrient management, it determines grain quality, yield, and resilience to stress, paying close attention to nutrient balance can mean the difference between a modest crop and a bumper harvest. Rice Nutrition encompasses macro‑nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, as well as micro‑elements such as zinc and iron that affect color, taste, and health benefits. The first step is to check the Soil Quality, the physical and chemical condition of the paddy field that supplies nutrients to the roots. Good soil texture, organic matter, and correct pH create a fertile platform where nutrients stay available for the plant.
Key Factors That Shape Rice Nutrition
Next, focus on Water Management, the control of irrigation, drainage, and flood timing that influences nutrient uptake and root health. Proper water depth during the vegetative stage keeps nitrogen soluble, while careful drainage before flowering prevents excess leaching of potassium. Another critical piece is Pest Management, the practice of monitoring and controlling insects, weeds, and diseases that can steal nutrients or damage plant tissue. A pest‑free crop uses more of the supplied fertilizer, translating into higher protein content in the grain. Finally, adopt Sustainable Farming, methods that preserve natural resources while maintaining productivity, such as integrated nutrient recycling and low‑input practices. When sustainability is built in, the soil stays fertile year after year, keeping rice nutrition stable without relying on costly chemicals.
Understanding these three pillars—soil, water, and pest control—helps you build a nutrient‑rich environment for rice. For example, a field with a pH of 5.5 to 6.5 holds phosphorus in a form the plant can absorb, while an aerobic irrigation schedule reduces methane emissions and keeps iron from becoming unavailable. Likewise, using bio‑fertilizers like rhizobium inoculants adds micro‑elements naturally, supporting the micro‑nutrient profile that many consumers look for today. Combining these tactics with regular soil testing creates a feedback loop: test, amend, test again, and watch the nutrient profile improve with each cycle.
Practical steps start with a simple soil test kit. Take samples from several spots, mix them, and send the composite to a local lab. Look for the nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) ratios, plus micronutrients like zinc (Zn) and manganese (Mn). If nitrogen is low, a split application of urea during tillering and panicle initiation can boost protein levels. If zinc is deficient, foliar sprays at the booting stage can correct the gap without over‑fertilizing the whole field. These targeted actions keep the input costs low while maximizing grain quality.
Water‑related decisions are just as data‑driven. Use a simple water level gauge to maintain 5‑10 cm depth during early growth, then lower it to 2‑3 cm before grain filling. This reduction helps the plant pull more nutrients into the grains instead of the straw. In regions with erratic rainfall, drip or laser‑levelled irrigation can provide the precision needed to keep nutrient concentrations steady. Monitoring the electrical conductivity (EC) of the water tells you whether salts are building up, which could block potassium uptake.
When pests strike, early detection saves nutrients. Set up yellow sticky traps for planthoppers, scout for rice blast lesions, and keep a weed‑free perimeter to stop competition for nutrients. If an outbreak occurs, opt for biopesticides or neem‑based formulations first; they control the pest while leaving beneficial microbes that aid nutrient cycling untouched. A healthy microbial community breaks down organic matter, releasing nitrogen in a plant‑ready form.
All these practices tie back to the core idea that rice nutrition is not a single action but a network of decisions that feed each other. By aligning soil amendments, water schedules, and pest strategies, you create a resilient system that delivers nutrient‑dense grain season after season. Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deeper into each of these topics—soil selection for rice, risk management in the rice business, sustainable techniques, and more—so you can start applying the right knowledge today.
5 Surprising Rice Facts You Should Know
Discover five eye‑opening rice facts covering production, types, water use, nutrition, and modern innovations that keep this staple grain vital worldwide.
About
Rice Cultivation
Latest Posts


Easy Ways to Loosen Compacted Soil Without Tilling
By Alden Thorne Jan 17, 2025

Discovering Native Indian Plants: A Seasonal Guide
By Alden Thorne Jan 17, 2025
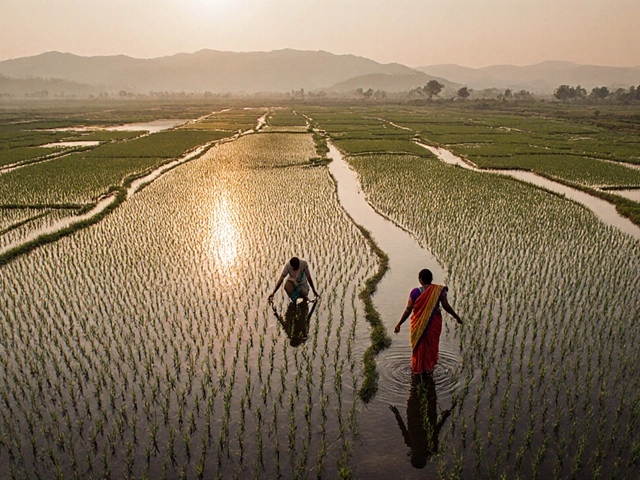

How Many Acres of Rice Are Needed to Feed One Person?
By Alden Thorne Oct 28, 2025