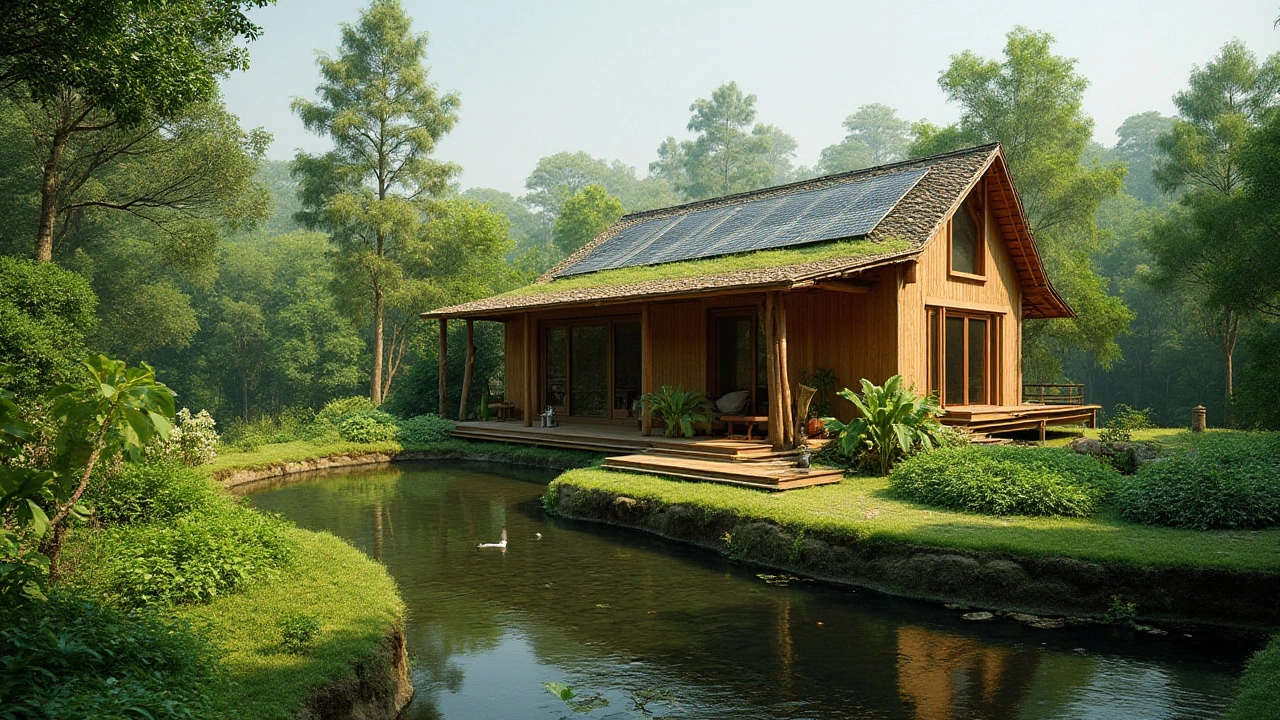
Creating a home that harmonizes with the environment is a vision many aspire to achieve. An eco-friendly house is not defined by a single aspect, like using solar panels or recycled materials, but by the integration of sustainable practices at every level of design and construction. This approach reduces negative environmental impact and promotes a healthier living space.
The journey towards building such a home involves understanding the interplay between architecture and nature. From choosing the right materials to incorporating natural elements, there are several paths one can take. Embracing these principles not only contributes to the planet's wellbeing but also enriches our own lives.
- Understanding Sustainable Building
- Common Materials and Their Benefits
- Innovative Home Designs
- Integrating Gardens with Architecture
- Energy Efficiency and Resource Conservation
- Long-term Benefits and Maintenance
Understanding Sustainable Building
In the pursuit of creating eco-friendly homes, understanding the essence of sustainable building is crucial. This approach to construction and design goes beyond superficial green practices by fostering a deep connection with the environment. The core idea is to create structures that are resource-efficient and naturally harmonious. A sustainable building is equipped to conserve energy, enhance the health of its occupants, and minimize the depletion of raw materials. One could argue that before laying a single brick, it is vital to conceptualize how each aspect of the home will impact both its immediate surroundings and the broader environment.
Nowadays, builders and architects are increasingly turning towards materials and technologies that support eco-friendly homes. The materials selected often play a dual role: they must not only be sustainable but also complement the local climate and geography. For instance, straw bale and cob have gained popularity in areas where they provide necessary insulation while being renewable. Similarly, using recycled steel or sustainably harvested timber can offer the robust structure needed, without guilt over unsustainable practices. Such materials not only reduce carbon footprints during construction but also ensure that the house remains energy-efficient over its lifetime.
"It is critical to recognize that sustainable building is not just a trend but a necessity," says environmental architect Jane Wenham-Jones. "Our decisions today lay the pathway for the future health of our planet."
This mindset shift is transforming how homes are designed. Incorporating renewable energy sources, like solar panels and wind turbines, is no longer just an alternative; it is rapidly becoming the norm. These technologies reduce reliance on fossil-fuel-based electricity and play a crucial role in achieving zero-energy buildings. The integration of smart home systems also boosts energy management, allowing homeowners to monitor and optimize their consumption. Technology, paired with thoughtful design, empowers residents to maintain an energy-efficient lifestyle effortlessly.
Another aspect of sustainable building is water conservation. With global water shortages becoming more pressing, methods to minimize usage and recycle water have become indispensable in modern home design. Techniques such as rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling systems ensure that every drop is utilized efficiently. Implementing systems that permit natural water management, like permeable pavements and green roofs, helps in managing stormwater and reducing strain on urban drainage systems.
A successful sustainable house must also connect with its natural surroundings. The layout and orientation of a house have profound effects on its energy consumption. By strategically positioning windows and designing open spaces for maximum natural light and ventilation, a home can significantly reduce its need for artificial lighting and climate control. This thoughtful design principle not only enhances aesthetics and comfort but also aligns with the ideals of green architecture, where the aim is to live in harmony with the Earth's rhythms.
Analyzing the long-term impacts and benefits is another layer of understanding sustainable building. The initial costs might appear higher than traditional building methods; however, the savings on energy, water, and maintenance over time often outweigh these costs. More importantly, the shift towards sustainable building practices is a commitment to leaving a healthier planet for future generations. Building an environmentally friendly home is not just about adopting new techniques—it's about adopting a new mindset.
Common Materials and Their Benefits
When venturing into the realm of building eco-friendly homes, the materials you select play a pivotal role in shaping both the sustainability and efficiency of the structure. Choosing the right supplies not only ensures longevity but optimizes the ecological footprint of your house. One of the leading materials in sustainable construction is bamboo. Known for its remarkable growth rate, bamboo regenerates faster than any traditional wood, making it a renewable resource. In addition to its rapid renewability, bamboo offers formidable strength, which is comparable to steel when considering tensile strength. This natural material provides a versatile solution for flooring and walls in green buildings.
Another fascinating material gaining traction is straw bale. It might conjure rustic images, but straw bale technology offers superior insulation properties. This not only cuts down the energy needed for heating and cooling but also uses a byproduct of grain agriculture, making it a sustainable choice. Straw bale homes offer an aesthetic appeal too, with their thick, rounded walls providing a subtle nod to traditional adobe designs. With the added benefit of excellent fire resistance due to its density, straw bale remains an attractive choice for those looking to build sustainable housing.
Green architecture often embraces cob, a centuries-old building material composed of subsoil, water, fibrous organic material (usually straw), and sometimes lime. With a history stretching back thousands of years, cob has been candidly lauded for its unique aesthetics and excellent thermal mass. These qualities are conducive to maintaining stable internal temperatures, reducing reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems. Resilient and natural, cob becomes an ally in managing resources efficiently while creating homes with character and distinction.
For those leaning toward innovative yet environmentally friendly house designs, reclaimed wood provides both sustainability and charm. Utilizing wood that would otherwise be destined for landfills gives new life to aged beams and panels, each with its own history. Reclaimed wood not only cuts down the demand for newly harvested timber but also adds rustic elegance and warmth to interiors. It's not uncommon to find homes where the careful use of reclaimed materials has been highlighted as an artistic feature, portraying a narrative of resourcefulness and commitment to sustainability.
"Reclaimed wood brings a depth and texture to homes that new lumber struggles to match. Its story is intertwined with the heart of sustainable architecture." – Architectural Digest
Beyond these materials, locally sourced stone provides an authenticity and strength that many architects favor in green buildings. The use of local stone minimizes transportation emissions, a significant factor in reducing environmental impact. It offers durability and thermal benefits akin to cob, ensuring homes require less energy to maintain comfortable temperatures throughout seasons. From flooring to walls and roofing, stone offers a multitude of applications in eco-conscious construction. Additionally, integrating local materials into house designs strengthens its sense of place and harmony with the surrounding environment.
Finally, recycled metal is becoming an essential component in sustainable construction. Whether it's using recycled steel for framing or aluminum for cladding, metals provide longevity and resilience while limiting the depletion of natural resources. Many sustainable building projects are finding innovative ways to incorporate these materials, simultaneously enhancing architectural integrity and environmental stewardship. On top of their practical benefits, recycled metals offer a sleek, modern aesthetic that aligns well with both traditional and contemporary design paradigms.
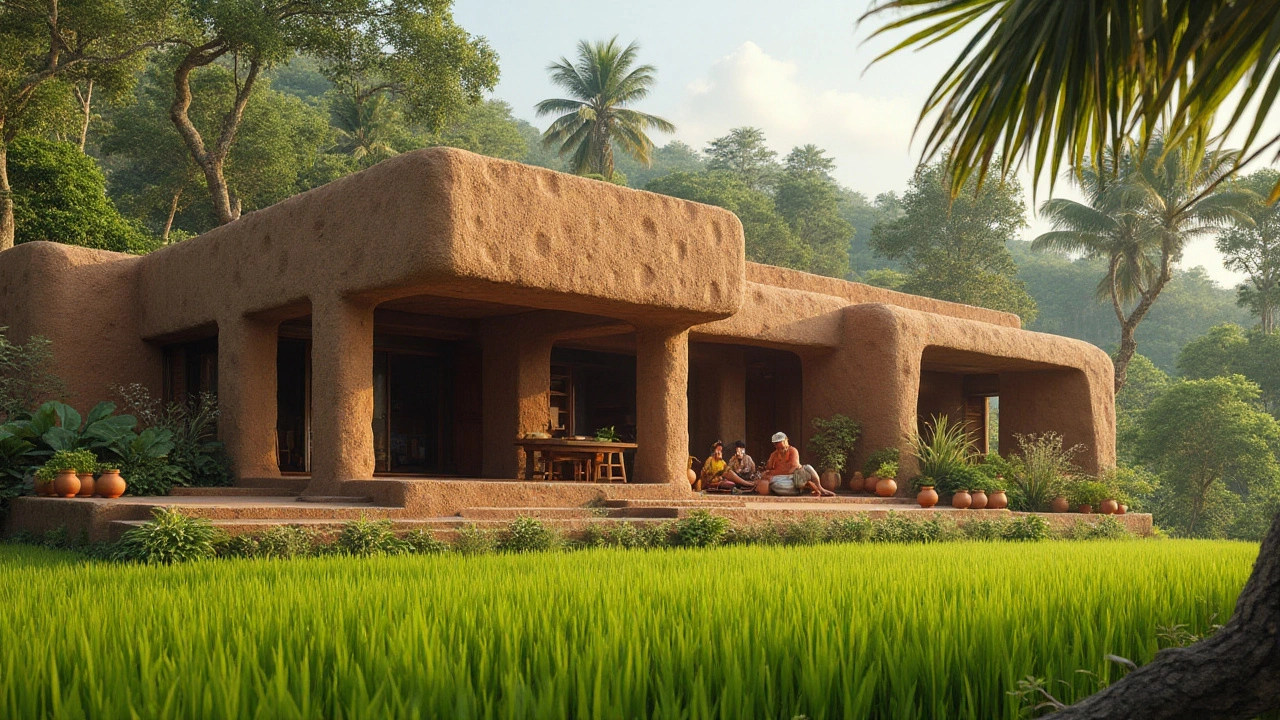

Innovative Home Designs
In recent years, the concept of eco-friendly homes has sparked a wave of architectural innovation that merges style with sustainability. These forward-thinking designs don't just seek to lessen environmental impact; they are also about enhancing how we live and interact with our surroundings. One standout example is the tiny house movement. Here, less is more, with spaces cleverly designed to maximize function without excessive square footage. This minimalistic approach not only reduces resource consumption during the build but also encourages a simpler, less cluttered lifestyle.
Then there are the increasingly popular earth-sheltered homes, which use the earth's natural insulation properties to maintain a stable internal climate. By being partially or completely covered by earth, these structures offer superior energy efficiency and create a tranquil living environment protected from extreme weather conditions. Beyond that, they blend seamlessly into the landscape, preserving the natural aesthetics of the area. Notably, these homes are often constructed with materials that are local and readily available, cutting down transportation emissions.
Another fascinating innovation is the use of reclaimed and recycled materials in modern house construction. Architects are increasingly incorporating elements like old shipping containers and reclaimed wood into their designs. This not only adds a unique charm to the home but also tackles the issue of waste. For example, using shipping containers as modular sections of a house can cut construction times and costs while significantly lowering the carbon footprint. These containers, once viewed merely as industrial remnants, are finding new life as components of stylish abodes.
Green architecture often takes cues from nature to improve efficiency and sustainability. Biomimicry in design—mimicking natural processes and ecosystems—has produced homes that use nature-inspired cooling and heating systems. For instance, some homes are designed with features that replicate termite mounds, which naturally regulate temperature without the need for artificial HVAC systems. This approach not only conserves energy but also maintains a healthy and balanced indoor environment.
"Adopting sustainable design principles is not just about reducing our carbon footprint, it's about creating buildings that positively impact the well-being of their inhabitants," says Richard Williams, a highly respected architect and advocate for sustainable architecture.
Of course, integrating technology is another hallmark of innovative sustainable building. Smart homes equipped with energy management systems can optimize energy use, automatically adjusting lighting, heating, and cooling based on real-time data. These homes often feature solar panels and advanced water recycling systems, enabling them to operate off-the-grid or in net-zero energy configurations. Such technological integration provides yet another layer of environmental and economic benefits, reducing dependency on nonrenewable energy sources.
Finally, open-plan layouts that prioritize natural light are a significant feature in these cutting-edge designs. Large, strategically placed windows and skylights can illuminate interiors throughout the day, reducing the need for artificial lighting. These homes not only cut down on energy costs but also create a healthier, more inviting living space that nurtures well-being. As we look toward the homes of tomorrow, the marriage of traditional building wisdom and modern technology continues to unlock new potentials for sustainable living.
Integrating Gardens with Architecture
When designing an eco-friendly home, integrating gardens with architecture is a crucial and fascinating endeavor. This fusion not only beautifies the living spaces but also serves functional purposes such as improving air quality and enhancing energy efficiency. The practice is rooted in creating a seamless connection between the natural and built environment, allowing the home to blend into its surroundings rather than stand apart as a separate entity. Garden roofs, vertical gardens, and courtyard designs are just a few examples of how this integration can take shape, achieving both aesthetic and functional benefits.
A well-planned garden integration strategy may involve planting native species that require less water and care, thereby conserving resources and promoting local biodiversity. Roof gardens and green walls can tremendously improve insulation, helping maintain indoor temperatures and reducing energy costs. The careful selection of plant species based on sunlight exposure and climate conditions adds layers of function and beauty, turning mundane spaces into vibrant ecosystems. This strategy not only makes homes more sustainable but also creates microhabitats that encourage the presence of beneficial insects and birds, contributing to a balanced urban environment.
Harnessing the principles of biophilia—our innate attraction to nature—can further enhance the integration process.
Famed architect Frank Lloyd Wright once said, "Study nature, love nature, stay close to nature. It will never fail you." This philosophy is at the heart of integrating gardens into architectural design, urging us to create spaces where nature and humans coexist harmoniously.A home that incorporates garden elements invites natural light and fresh air, encouraging a healthy lifestyle. Such homes foster a deeper connection to nature, offering psychological benefits like reduced stress and increased productivity.
For a practical approach, homeowners might consider outdoor rooms or spaces where the indoor and outdoor blend seamlessly, such as patios surrounded by lush greenery or kitchens that open into herb gardens. Utilizing edible landscaping, where fruits and vegetables take the place of ornamental plants, can transform gardens into year-round food sources. This approach aligns with self-sufficiency and teaching sustainable habits to future generations. Additionally, rain gardens and water collection systems can be cleverly integrated to manage stormwater, preventing flooding while irrigating plants naturally.
To illustrate the potential impact, consider this data:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Green Roof | Reduces heating needs by 25% |
| Vertical Garden | Improves indoor air quality by 30% |

Energy Efficiency and Resource Conservation
When building an eco-friendly home, energy efficiency and resource conservation play crucial roles in reducing environmental impact. Energy efficiency means using less energy to perform the same tasks, which contributes to decreasing your carbon footprint while saving money over the long term. Selecting appropriate materials and designs can immensely help in achieving these goals. For example, using high-performance insulation and windows that minimize air leakage can help maintain a comfortable indoor climate without relying heavily on heating or cooling systems.
Another effective strategy is the use of passive solar design. This involves positioning the house to maximize the use of natural sunlight, effectively harnessing the sun's energy to provide natural light and heating. By integrating large south-facing windows and thermal mass materials like concrete or stone, the home can store and slowly release heat during cooler periods. A well-designed passive solar home captures 20-30% more light during the winter months, reducing the need for artificial heating.
Water conservation is another significant aspect of creating an environmentally friendly house. Low-flow fixtures and dual-flush toilets are practical solutions that substantially reduce water usage. Rainwater harvesting systems can be incorporated for collecting rain from rooftops, which can then be used for landscaping or even household needs after appropriate filtering. A typical rainwater catchment system can collect around 600 gallons from a single inch of rain on a 1,000-square-foot roof.
The importance of selecting sustainable materials cannot be overstated. Materials like bamboo and reclaimed wood are not only beautiful but also rapidly renewable. Moreover, utilizing recycled materials, such as steel or recycled composites, significantly cuts down on the environmental toll of new resource extraction. A significant portion of energy consumption during construction comes from transporting heavy materials, so sourcing locally can also make a big impact.
Improving energy efficiency often involves integrating technology into the home. Smart home systems enable homeowners to monitor and optimize energy use in real time. Thermostats that learn your routine and adjust heating and cooling accordingly can cut HVAC costs by up to 20%. Lighting systems that automatically turn off when not in use also contribute to reducing electricity usage. According to the Department of Energy, adopting these efficient systems could save the average household about $100 to $200 annually.
“For the typical U.S. household, electricity usage makes up about 81% of a home's energy use. Being smart about the way you use your energy can help you save money and help you keep your house comfortable,” says the U.S. Department of Energy.
When these solutions are put into practice, the long-term benefits include not only significant reductions in energy costs but also a smaller ecological footprint. These measures make it possible to live in harmony with the environment, ensuring resources are used wisely and preserved for the future generations. The transition towards more efficient and resource-conscious living requires a mix of vision, technology, and a commitment to sustainable practices.
Long-term Benefits and Maintenance
When you commit to building an environmentally friendly house, you're not just making a choice for today, but embarking on a journey with lasting rewards. One of the primary benefits of such an endeavor is a significant reduction in utility costs. Homes constructed using sustainable materials and designs often utilize natural resources more efficiently, leading to lower energy consumption. For instance, solar panels can drastically cut electricity expenses, and rainwater harvesting systems can provide a sustainable water supply, saving on water bills. Over time, these savings can offset the initial investment in eco-friendly technology and materials.
Aside from financial savings, sustainable homes offer health advantages that are less tangible but equally important. Natural building materials like wood, straw bales, and cob are devoid of the harmful chemicals found in conventional construction materials. These toxins can contribute to indoor air pollution, causing respiratory problems. By choosing materials that allow walls to 'breathe', you're promoting better air quality within your living spaces, which can lead to fewer allergies and a more pleasant living environment.
"The long-term financial and health benefits of sustainable design can balance or exceed the initial costs," says Lisa Gartland, an expert in sustainable architecture. "It’s about investing in the future for a healthier planet and population."
Maintenance for eco-friendly homes can differ from standard buildings, often requiring less routine upkeep. Structures such as green roofs not only insulate homes, reducing heating and cooling costs, but also extend the lifespan of the roof by protecting it from weather damage. Meanwhile, due to their durability and resilience, materials like bamboo and recycled metal often tend to require less frequent repairs and replacements. When maintenance is needed, it can typically be less invasive and less frequent, thanks to the durability of such materials.
Environmental Impact and Community Benefits
Eco-friendly homes contribute positively to the environment, a legacy that extends far beyond the walls of a single home. Living in a sustainably designed home often fosters a deeper connection with the surrounding community. Engaging in community gardens or shared green spaces not only improves local biodiversity but also supports a network of people dedicated to sustainability. This shared commitment can inspire communal efforts, such as local composting initiatives or energy-sharing programs, which amplify the impact of individual eco-friendly homes on a broader scale.There is a growing body of evidence suggesting that people living in energy-efficient, sustainable housing enjoy a higher quality of life. According to a study by the National Association of Home Builders, homeowners in greener homes report higher satisfaction in areas such as comfort, functionality, and aesthetics. Additionally, eco-friendly houses can often command a premium price on the market, making them a wise investment for those looking to increase the long-term value of their property.
Cost Effectiveness and Tax Incentives
It is also worth considering the financial benefits offered by governments and organizations to encourage the construction of such homes. Many regions offer tax incentives, grants, or low-interest loans to support initial investments in green homes. These incentives can play a crucial role in making eco-friendly housing more accessible to a wider range of people. Some governments have implemented policies that reward homeowners who achieve certain energy efficiency standards, offering rebates or other forms of financial support. Such initiatives not only make sustainable housing more financially viable but also reinforce its position as a smart long-term investment.By embracing the concept of eco-friendly homes, the cumulative benefits extend across personal, financial, and societal realms, painting a picture of a sustainable future that is both achievable and beneficial to all.